A Complete Guide ToSurface Test Tree
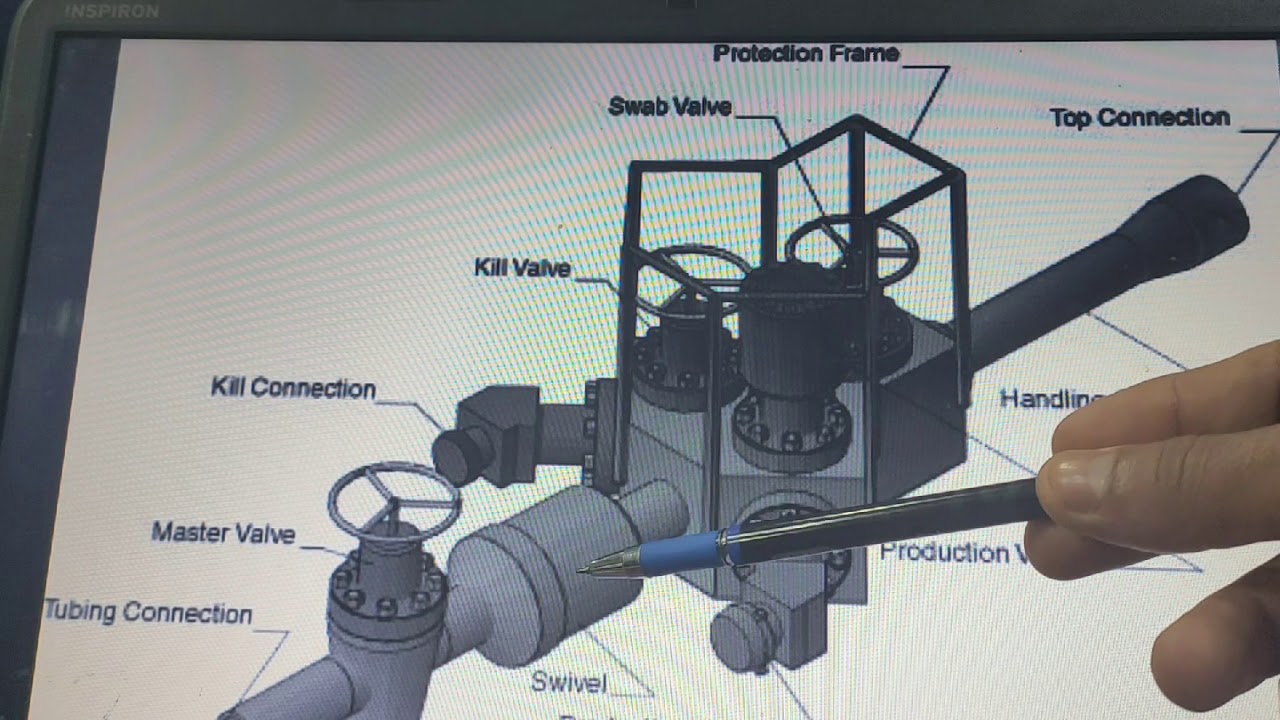
The Surface test tree, also known as the flow head, is the first piece of equipment through which fluid from the well travels. It is positioned directly on top of the well. Its main job is to regulate the flow of fluid into and out of the well. Through the use of a crossover sub, the surface test tree can be altered to connect to various sizes of tubing or drill pipe.
What is a surface test tree?
When completing, testing, or performing live well intervention activities, the surface test tree supports the test string and provides a mechanism of surface well management. To control the flow of wellbore fluids, two off-wing valves are connected to the kill and flow manifolds.There are four gate valves in the flow head: a master valve, two wing valves, and a swab valve.
A swivel beneath the main block of the flow head allows the drill stem to freely spin while the test tree remains stationary. There’s also a kind that has a mater valve beneath the swivel.
A handle sub is included with each tree, allowing rig elevators to raise and lower the tree in the derrick. Flexible flow lines can be easily attached to the surface test tree thanks to flanged 45° support subs on the kill and flow wing sides of the central body.

Application
- Pre-completion testing
- Drill stem testing
- Well cleanup
- Well simulation
- Onshore and offshore well testing
Design Code and its standards
- Enhances the text string weight.
- The main block’s protection structure for manual and hydraulic valves improves durability.
- On the intake of the killing line, a flapper or dart valve is installed.
- The master valve can be placed underneath or inserted in the main block
- Swivel in the surface test tree permits the text string to rotate and detach operations for packer setup.
- Flexibility and mobility are provided by a compact design.
In conclusion, at least two surface pressure barriers are provided by the surface test tree. Swivel enables string rotation without turning the flow head, allowing connection to a kill line for the testing of pressure, injection, or killing of wells and allows instruments to run through the swab valve and to run into the well.



